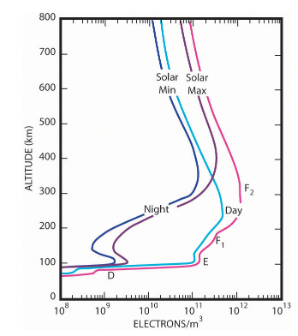
The electromagnetic radiation from the sun interacting with the upper atmosphere generates ions distributed over different density and energy layers, forming the ionosphere (50 to 500 km). The variation over time and space of the electronic density of the ionosphere, directly linked with solar activity, affects the telecommunication and observation services. Thus, understanding and monitoring the ionosphere is the best way to keep ground and space-based systems operating.
The CUIONO instrument, developed at ONERA, is mainly composed of a RF antenna and a software defined radio (SDR) card on board a Cubesat. Together with a ground-based sounder emitting RF signal between 8 and 23 MHz, the full setup can characterize the ionosphere.
A first model of this instrument is being developed for integration to the INSPIRE-Sat 7 mission in collaboration with LATMOS [1]. The 2U satellite as been launched on April 15th 2023, carrying multiple instruments to measure the Earth’s energy budget for climate change studies. First contact has been made with CUIONO and data has been recorded ! More information available on the press release (fr).
A second model, with advanced features, is planned to be part of the Flylab mission.
Finally, a third one is planned to fly onboard the ASTERIX mission, still under definition.
| Left, variation of the electronic density with the altitude, measured by an experimental setup such as CUIONO. Right, components and functions included in CUIONO model developed for the Flylab mission. The first model dedicated to INSPIRE-Sat 7 does not include the GPS signal and PPS function. | ||
[1] Meftah, M. et al., INSPIRE-SAT 7, a Second CubeSat to Measure the Earth’s Energy Budget and to Probe the Ionosphere. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010186